Atrial Fibrillation
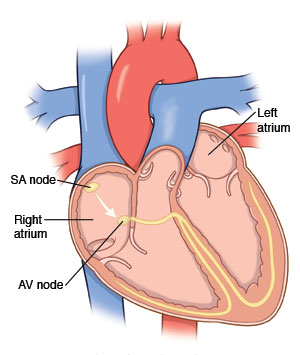
May 16, 2023Atrial fibrillation is a condition in which the heart beats in an irregular pattern. It is the most common abnormal heart rhythm. It is caused by a problem in the heart's electrical pathways within the muscle of the upper chambers of the heart (atria). It can be a sign of heart disease or other health problems that affect the heart.
Heart palpitations are a common symptom of atrial fibrillation. This is the feeling that your heart is fluttering, or beating fast, hard, or irregular. When the heart beats too fast, it doesn't pump blood very well. This can cause other symptoms, such as anxiety, fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, or fainting. Atrial fibrillation may come and go on its own, which is known as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. It can last from a few hours to a couple of days. Or it may become persistent, lasting for weeks or months at a time. It can even become lifelong (permanent). Some symptoms of atrial fibrillation are hard to notice. For instance, some people develop subtle fatigue. Others notice a reduced ability to exercise. Some people have no symptoms.
Atrial fibrillation is more common in older adults. It may be caused by heart disease or other conditions in the body that affect the heart. They include:
-
Coronary artery disease (atherosclerosis), sometimes called blocked arteries
-
High blood pressure
-
Disease of the heart valves
-
Enlarged heart
-
Heart failure
Atrial fibrillation can also occur without heart disease because of:
-
Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroid)
-
Chronic lung disease (COPD, emphysema, or bronchitis)
-
Heavy alcohol use
-
Heart stimulants, such as cocaine, amphetamines, diet pills, certain decongestant cold medicines, caffeine, or nicotine
-
Infection
-
Blood clot in the lung (pulmonary embolus)
-
Diabetes
-
Chronic kidney disease
-
Obesity
-
Obstructive sleep apnea
-
Extreme and continued athletic conditioning
-
Certain genetic diseases
Treating or removing these causes will help your treatment for atrial fibrillation. It will also make it less likely for it to come back.
Atrial fibrillation can alternate back and forth with another abnormal rhythm called atrial flutter. Atrial flutter is a more regular heart rhythm. It is also linked to an increased risk for stroke. Correct treatment of these arrhythmias can lower your risk for stroke.
Home care
Follow these guidelines when caring for yourself at home:
-
Go back to your usual activities as soon as you are feeling back to normal.
-
If you smoke, stop smoking. Contact your healthcare provider or a local stop-smoking program for help.
-
Don't use stimulants like alcohol, cocaine, amphetamines, diet pills, certain decongestant cold medicines, caffeine, or nicotine.
-
If your provider prescribed medicine to stop atrial fibrillation from coming back, take it exactly as directed. Some medicines must be taken every day, not just when you have symptoms. This will help them work as they should.
-
If you were prescribed a blood-thinning medicine, take it exactly as prescribed. One of these medicines, called warfarin, needs your blood to be tested regularly as advised by your healthcare provider. This will make sure you are getting the dose that is right for you. It also lowers your risk for side effects. You may have been prescribed other blood-thinning medicines that don't need regular testing.
Follow-up care
Follow up with your healthcare provider as advised.
When to get medical care
Call your healthcare provider if any of these occur:
-
Swelling in the legs that gets worse
-
Unexpected weight gain
-
Pain, redness, or swelling in 1 leg
Call 911
Calling
Call
-
Weakness of an arm, leg, one side of the face
-
Chest pain
-
Shortness of breath, or feeling that you can't get enough air
-
Feeling lightheaded, faint, or dizzy
-
Your heartbeat is very fast, slow, or irregular compared with your regular heartbeat
-
Uncontrolled bleeding
-
Trouble with speech or vision
-
Extreme drowsiness, confusion, dizziness, or fainting